What is a prime number:
A number is called prime if that number is divisible by 1 and the number itself. For example, 2, 3, 5, 7, etc. are prime numbers. In this post, I will show you how to check if a number is prime or not in JavaScript with examples.
Method 1: By using a for loop:
This is the simplest way to find a prime number. We will write one loop that will iterate from 2 to number/2. On each iteration, we will check if the current value of the loop variable can divide the given number or not. If it can divide, it is not a prime number. If we don’t find any value in the loop that can divide the number, it is a prime number.
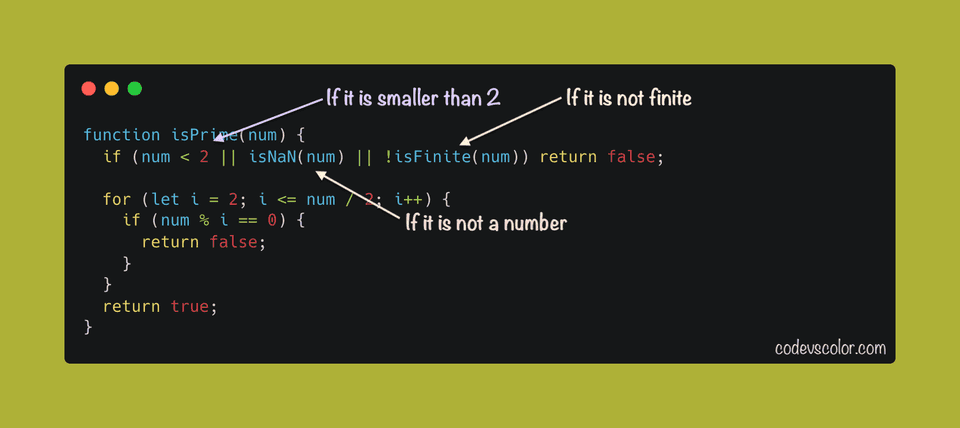
function isPrime(num) {
if (num < 2 || isNaN(num) || !isFinite(num)) return false;
for (let i = 2; i <= num / 2; i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
console.log(isPrime(2));
console.log(isPrime(53));Download it on GitHub
Explanation:
- The
isPrimemethod is used to check if a number is prime or not. It takes one numbernumas its parameter and returns one boolean value based on whether the parameter is a prime number or not. - If the value of
numis less than 2 or if it is not a number or if it is not a finite value it returnsfalse. - The
forloop iterates from 2 tonum/2and if any number can dividenum, it returnsfalse. - At the end of the method, it returns
truei.e. no number is found in the loop that can divide the given number.
Method 2: By iterating up to the square root of the number:
With this method, the loop will iterate up to the square root of the number. We can find all the divisors of a number if we iterate up to the square root of that number. With this approach, we can reduce the iteration number of the loop.
function isPrime(num) {
if (num < 2 || isNaN(num) || !isFinite(num)) return false;
for (let i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
console.log(isPrime(2));
console.log(isPrime(53));Download it on GitHub
We are using the Math.sqrt method to find the square root of the number num. It will print similar results.
Method 3: By iterating over the odd numbers:
With this approach, we will first check if the number is divisible by 2 or not. If it is not divisible by 2, we will iterate over the odd numbers from 3 to the square root of the number.
function isPrime(num) {
if (num < 2 || isNaN(num) || !isFinite(num)) return false;
if (num % 2 == 0) return num == 2;
for (let i = 3; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i += 2) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
console.log(isPrime(2));
console.log(isPrime(53));Download it on GitHub
- It checks if the value of
numis divisible by 2 or not. If yes, it returnstrueonly ifnumis equal to 2. - The
forloop iterates from 3 and on each step, it increments the value ofiby 2 i.e. it iterates over the odd numbers.
It will print similar results.
Method 4: By jumping between the numbers:
We can represent any prime number as 6i ± 1, where i is any integer value. Only 2 and 3 are excluded from this formula. This approach will first check if the number is divisible by 2 or 3. If it is not, it will start the loop from i = 5, and on each iteration, it will increment its value by 6. If i or i + 2 can divide the number, it won’t be a prime number.
function isPrime(num) {
if (num < 2 || isNaN(num) || !isFinite(num)) return false;
if (num % 2 == 0) return num == 2;
if (num % 3 == 0) return num == 3;
for (let i = 5; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i += 6) {
if (num % i == 0 || num % (i + 2) == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
console.log(isPrime(2));
console.log(isPrime(53));Download it on GitHub
It will print the same result.
Finding all prime numbers in between 1 to 100:
We can use any of the above methods with a loop to find out all prime numbers between 1 to 100 or in any range:
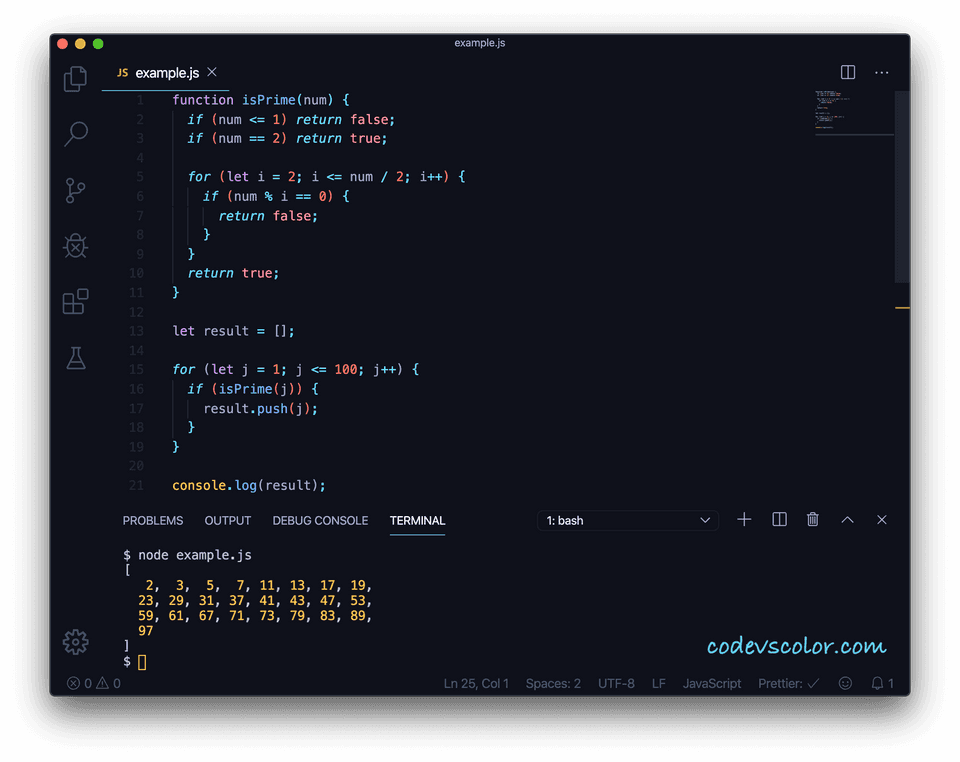
function isPrime(num) {
if (num <= 1) return false;
if (num == 2) return true;
for (let i = 2; i <= num / 2; i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
let result = [];
for (let j = 1; j <= 100; j++) {
if (isPrime(j)) {
result.push(j);
}
}
console.log(result);Download it on GitHub
Here, we are calling the isPrime method to check if a number is prime or not. The for loop runs from j = 1 to j = 100 and appends all prime numbers to the array result.
It will print the below output:
[
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71,
73, 79, 83, 89, 97,
];Similar tutorials:
- Javascript Array splice and slice method explanation with examples
- Count specific character occurrence in a string in Javascript
- How to compare two dates in JavaScript
- JavaScript Date getter methods for normal date and UTC date
- Setter methods in JavaScript normal date and UTC date
- Javascript string indexOf() method explanation with example