C# program to print the Arithmetic progression series, AP:
In this post, we will learn how to print the Arithmetic progression series in C#. The AP or Arithmetic progression series is a sequence of numbers where the difference between two numbers is constant. This is called common difference.
If the first number of the AP series is a and common difference is d, then the nth number of the Arithmetic progression series is:
a + (n - 1)*dThe program will take the values of a, n and d from the user and print the first n numbers of the AP series.
We can use any loop like for loop or while loop to print the series. We can also use a recursive method to do the same.
Method 1: C# program to print the Arithmetic progression series by using a for loop:
In this C# program, we will use a for loop to print the Arithmetic progression series. This program will take the values of a, n and d as inputs from the user and it will print the AP series.
Below is the complete program:
using System;
namespace Program
{
class Program
{
static void PrintAP(int a, int d, int n)
{
int NthValue = a + (n - 1) * d;
for (int i = a; i <= NthValue; i = i + d)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", i);
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, n, d;
Console.WriteLine("Enter the total count of numbers to print: ");
n = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the starting number: ");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the common difference: ");
d = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
PrintAP(a, d, n);
}
}
}Here,
- PrintAP method is used to print the AP series. It takes a, d and n as the parameters.
- The nth value is calculated before for loop is started. It is stored in NthValue variable.
- The for loop runs from i = a to i = NthValue, i.e. it starts from the start value of the series and ends at nth value. On each iteration, we are incrementing the value of i by d or it is incremented by common difference.
- Inside the loop, the value of i is printed which are the numbers of the AP series.
- The values of n, a and d are taken as user inputs and PrintAP is called to print the series.
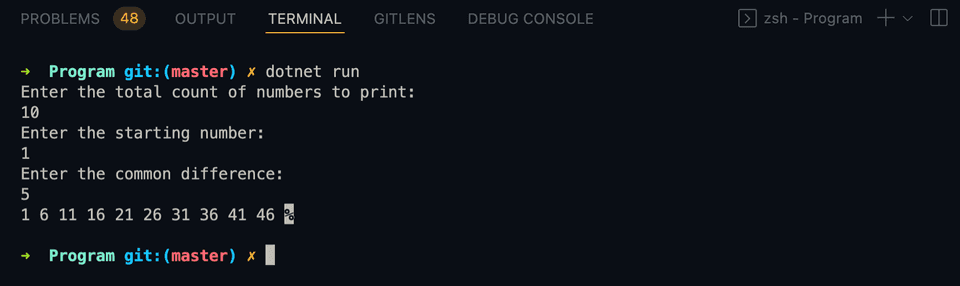
If you run this program, it will give output as like below:
Enter the total count of numbers to print:
10
Enter the starting number:
1
Enter the common difference:
5
1 6 11 16 21 26 31 36 41 46We can also avoid the calculation of the nth value and decrement the value of n by 1 on each iteration. The second condition of the for loop will be to check if the value of n is greater than 0 or not.
using System;
namespace Program
{
class Program
{
static void printAP(int a, int d, int n)
{
for (int i = a; n > 0; i = i + d)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", i);
n--;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, n, d;
Console.WriteLine("Enter the total count of numbers to print: ");
n = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the starting number: ");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the common difference: ");
d = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
printAP(a, d, n);
}
}
}It will print the first n values of the AP series.
Method 2: C# program to print the Arithmetic progression series by using a while loop:
Another way is to use a while loop to print the AP series. Let me change the above program to use a while loop instead of a for loop:
using System;
namespace Program
{
class Program
{
static void printAP(int a, int d, int n)
{
int CurrentValue = a;
while (n > 0)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", CurrentValue);
n--;
CurrentValue += d;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, n, d;
Console.WriteLine("Enter the total count of numbers to print: ");
n = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the starting number: ");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the common difference: ");
d = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
printAP(a, d, n);
}
}
}The while loop will run while the value of n is greater than 0. On each iteration, it prints the CurrentValue, which is initialized as a at the beginning of the program.
Also, the value of n is decremented by 1 and the value of CurrentValue is incremented by d at the end of each iteration. So, the loop will stop at n = 0 and CurrentValue will point to the next value of the series.
Method 3: C# program to print the Arithmetic progression series by using a recursive method:
Another way is to use a recursive method. A method is called a recursive method if the method calls itself again and again to find a result.
using System;
namespace Program
{
class Program
{
static void printAP(int CurrentValue, int d, int n)
{
if (n == 0) return;
Console.Write("{0} ", CurrentValue);
printAP(CurrentValue + d, d, n - 1);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, n, d;
Console.WriteLine("Enter the total count of numbers to print: ");
n = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the starting number: ");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the common difference: ");
d = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
printAP(a, d, n);
}
}
}- We changed the printAP method to a recursive method.
- It takes three parameters, the current value to print, the common difference, and the total numbers to print.
- On each recursive call, the current value is updated, i.e. the common difference is added to it to get the next value of the series. Also, the value of n is decremented by 1.
- It will stop once the value of n becomes 0.
You will get a similar result with this program as well.
You might also like:
- C# program to create an array of objects
- 4 different C# programs to convert a decimal number to binary
- C# program to convert a binary value to decimal
- C# program to print the result of the division of two numbers
- 3 different C# programs to print the name and age of a user
- 3 ways in C# to find the sum and average of user input numbers
- 4 ways to print the Fibonacci series in C#
- 4 ways in C# to find the sum of first n numbers of the Fibonacci series
- 3 ways to find the nth number of the Fibonacci series